The pages of the Bible are intertwined with the rise and fall of ancient empires that exerted significant influence over the land of Israel and the course of biblical history. From the mighty Babylonian Empire to the expansive Roman Empire, these imperial powers shaped the political, cultural, and religious landscape of the ancient Near East. In this article, we will explore the impact of empires on biblical history, tracing their influence from Babylon to Rome and beyond.
The Babylonian Empire:
The Babylonian Empire, under the rule of kings such as Nebuchadnezzar II, played a pivotal role in the biblical narrative, particularly during the period of the Babylonian exile. In 586 BCE, Nebuchadnezzar's army besieged Jerusalem, destroyed the Temple, and deported the Jewish population to Babylon. This event, known as the Babylonian Captivity, had profound implications for the religious identity of the Jewish people and gave rise to prophetic literature condemning the sins of Israel.
The Persian Empire:
Following the fall of Babylon, the Persian Empire emerged as a dominant force in the ancient Near East. Under the rule of Cyrus the Great, the Persians conquered Babylon and allowed the exiled Jews to return to their homeland and rebuild the Temple in Jerusalem. This period of Persian rule marked a significant turning point in biblical history, as it facilitated the restoration of Jewish religious and cultural life in the land of Israel.
The Hellenistic Period:
The conquests of Alexander the Great in the 4th century BCE ushered in the Hellenistic era, during which Greek culture and influence spread throughout the Near East. The Hellenistic period had a profound impact on Jewish society, leading to the translation of the Hebrew Bible into Greek (the Septuagint) and the emergence of Hellenistic Jewish literature. The struggles between Hellenistic rulers such as the Seleucids and the Jewish Maccabees are chronicled in the books of Maccabees and provide important historical context for understanding the events leading up to the birth of Jesus Christ.
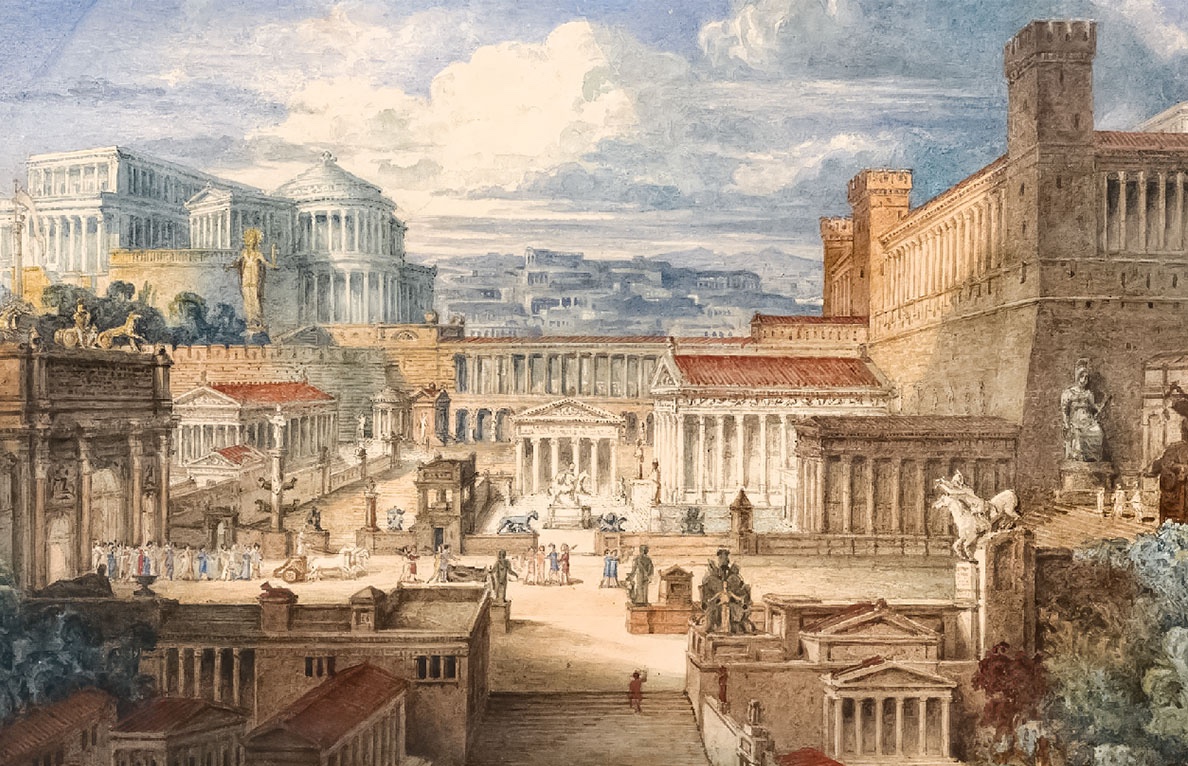
The Roman Empire:
By the 1st century CE, the Roman Empire had become the dominant power in the Mediterranean world, including the land of Israel. Roman rule brought stability and infrastructure to the region but also sparked tensions and conflicts, particularly between the Jewish people and their Roman overlords. The crucifixion of Jesus Christ under the authority of the Roman governor Pontius Pilate and the subsequent spread of Christianity throughout the Roman Empire are key events that shaped the course of biblical history.
The influence of empires on biblical history is a testament to the interconnectedness of politics, culture, and religion in the ancient world. From Babylon to Rome, imperial powers left an indelible mark on the land of Israel and the development of Judeo-Christian civilization. By understanding the role of empires in biblical history, we gain insights into the complex dynamics of power, faith, and human agency that continue to shape our world today.