Jerusalem, often referred to as the "City of David," stands as one of the oldest and most historically significant cities in the world. Its ancient streets bear witness to thousands of years of human civilization, religious devotion, and geopolitical upheaval. Through the lens of archaeology, we can uncover the layers of Jerusalem's rich history and gain a deeper understanding of the city's profound significance.
Exploring Ancient Jerusalem:
The archaeological exploration of Jerusalem has unearthed a wealth of discoveries that shed light on the city's past. Excavations in and around the Old City have revealed evidence of ancient settlements dating back to the Bronze Age, including remnants of fortifications, palaces, and residential areas.
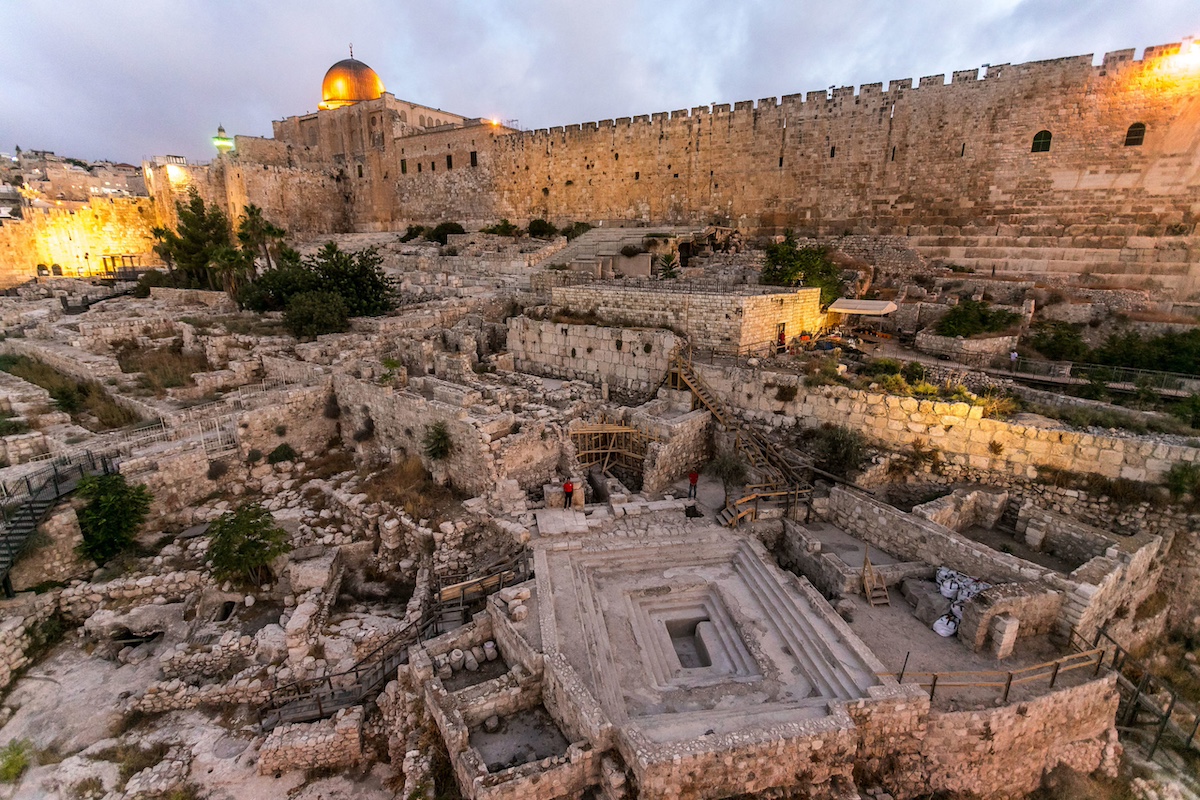
One of the most iconic archaeological sites in Jerusalem is the City of David, located just south of the Temple Mount. Here, excavations have revealed the remains of the ancient Israelite capital, including the impressive Stepped Stone Structure and the Gihon Spring, which served as the city's primary water source.
The Temple Mount itself is a treasure trove of archaeological remains, encompassing the Western Wall, the Dome of the Rock, and the Al-Aqsa Mosque. Beneath the surface lie layers of history spanning thousands of years, from the First Temple period to the present day.
Uncovering Biblical Jerusalem:
Many archaeological discoveries in Jerusalem have direct connections to events and figures described in the Bible. The discovery of Hezekiah's Tunnel, a remarkable engineering feat from the 8th century BCE, corroborates the biblical account of King Hezekiah's efforts to fortify the city's water supply during the Assyrian siege.
Excavations in the City of David have also uncovered artifacts and inscriptions that provide insights into the lives of biblical figures such as King David and King Solomon. The Ophel Inscription, discovered near the Temple Mount, bears the earliest known reference to the city of Jerusalem outside of the Bible.
Challenges and Controversies:
The archaeological exploration of Jerusalem is not without its challenges and controversies. The city's complex political and religious landscape, coupled with ongoing tensions in the region, present obstacles to excavation and research. Additionally, competing interpretations of archaeological findings can sometimes lead to contentious debates about the city's history and significance.
Looking to the Future:
Despite these challenges, archaeologists continue to uncover new discoveries and push the boundaries of our understanding of Jerusalem's past. Advances in technology, such as remote sensing and 3D imaging, offer new opportunities for non-invasive exploration and data analysis.
As we dig deeper into the archaeology of Jerusalem, we not only uncover the physical remains of the past but also glimpse the enduring legacy of a city that has shaped the course of human history. Through continued research and exploration, we can gain a deeper appreciation for Jerusalem's rich heritage and its significance as a cultural, religious, and historical treasure.